 INFRA
INFRA
 INFRA
INFRA
 INFRA
INFRA
With a nearly $60 billion revenue run rate, growing at 14% and throwing off more than $5 billion in operating cash last quarter, Cisco Systems Inc. has an awesome business.
But customers are vocal about the complexity of Cisco’s portfolio and, if their concerns are not addressed head on, the company risks encountering friction beyond just economic headwinds. We believe Cisco’s challenges are most decidedly not product breadth and depth. Rather, the company’s mandate is to integrate the piece parts of its intricate offerings to create more facile and seamless experiences for customers.
In this Breaking Analysis and ahead of Cisco Live in Las Vegas June 4-8, we dig deeper into Cisco’s business and double-click on three key areas of its portfolio: 1) security; 2) networking; and 3) observability. We have spending data from Enterprise Technology Research and a guest appearance from SiliconANGLE contributor and market watcher Zeus Kerravala, principal at ZK Research.
Let’s start by doing some stock market comparisons.
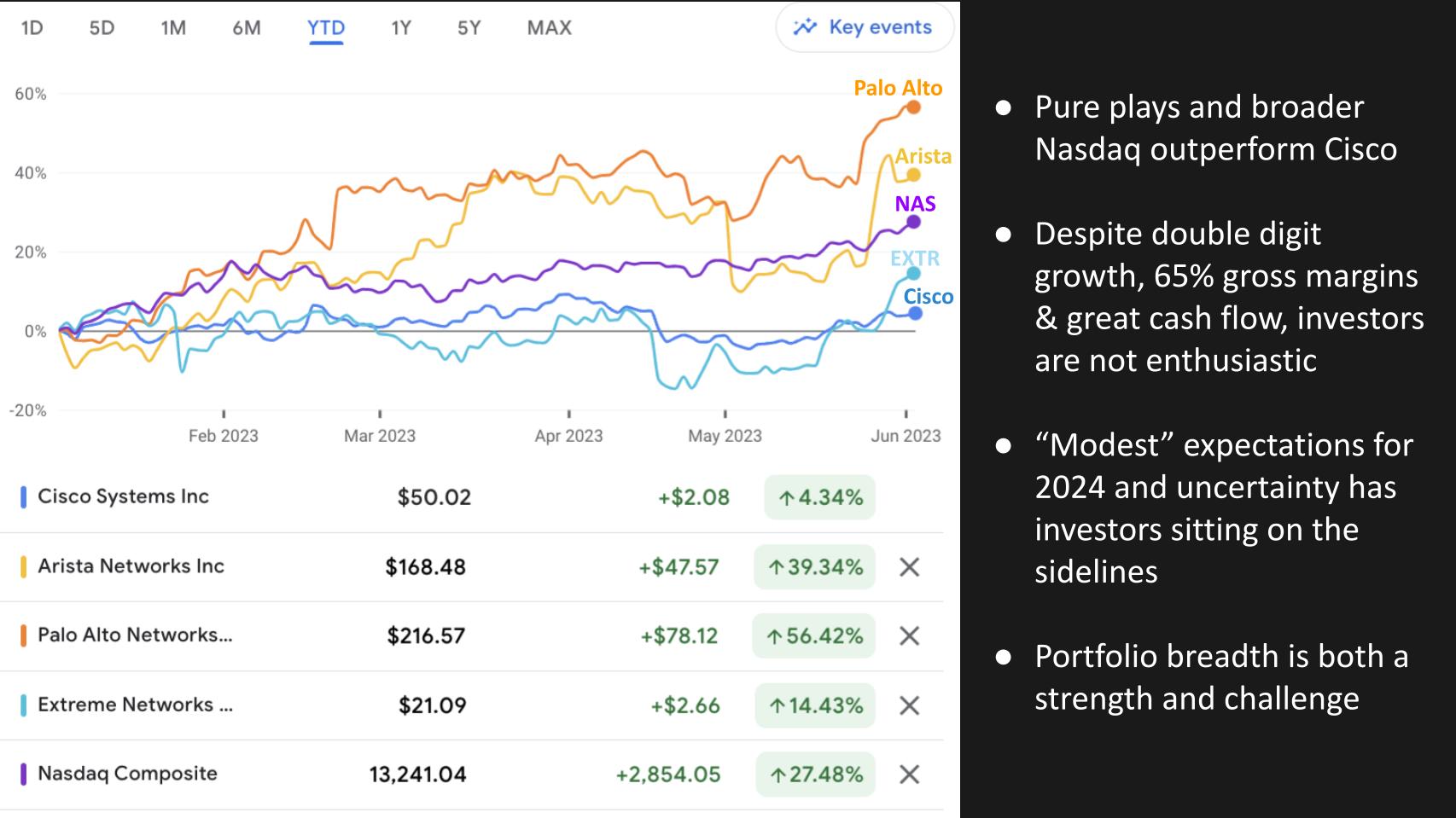
The chart above shows year-to-date comparisons among Cisco, Palo Alto Networks Inc., Arista Networks Inc., Extreme Networks Inc. and the Nasdaq Composite. As you can see, the pure plays, as well as the NAS, are outperforming Cisco by a wide margin. That’s despite Cisco’s double-digit growth last quarter, 65% growth margins and a $200 billion market cap.
The reason is Chief Executive Chuck Robbins set modest expectations for 2024, which, when modeled out relative to Cisco’s longer-term outlook, suggest slowing momentum in the near- to mid-term. In addition, we believe the breadth of Cisco’s portfolio, while a key strength, also creates adoption challenges for the company’s customers.
What follows is a summary of how Kerravala interprets this data.
Kerravala sees this data as a nuanced comparison between Cisco, a behemoth with an impressive cash generation capability, and smaller companies such as Arista and Extreme. Despite acknowledging the somewhat fair comparison, he suggests that Cisco is handicapped because smaller entities may capture the benefits of a market trend more swiftly, Cisco’s broad scope often hampers its ability to do so. But Cisco throws off more operating cash in a quarter than these companies generate in annual revenue.
He used the example of Zoom Video Communications Inc. and RingCentral Inc., noting how Cisco’s performance paled in comparison two years ago, but the tide has turned since then, with the unified communications sector waning, but Cisco thriving in relative terms.
Kerravala believes Cisco’s breadth and stability make it a safe investment bet, but its size prevents it from realizing the rapid growth that smaller, more specialized companies can. The broad spectrum of markets that Cisco operates in implies a reduced likelihood of success across all these fronts simultaneously.
Watch Zeus Kerravala comment on the comparisons between Cisco and the pure plays.
The table below represents the contribution of Cisco’s lines of business as reported in its financials. As we said at the top, 14% revenue growth is pretty astounding for a company of Cisco’s size. With tough comps ahead, it’s unlikely Cisco can keep up this pace.
Networking makes up more than half of Cisco’s revenue, but the company is growing its software contribution, which is just under 30% today, and its annual recurring revenue accounts for more than 40% of revenue, which gives the company better visibility on the future. This all helps prop up Cisco’s alluring 65%-plus gross margin model, which unlike many of its large incumbent competitors has held up well over decades. Moreover, Cisco’s shift to a recurring revenue and subscription model has been executed quite well compared with many firms (some much smaller, such as Splunk Inc.), which have struggled with that transition.
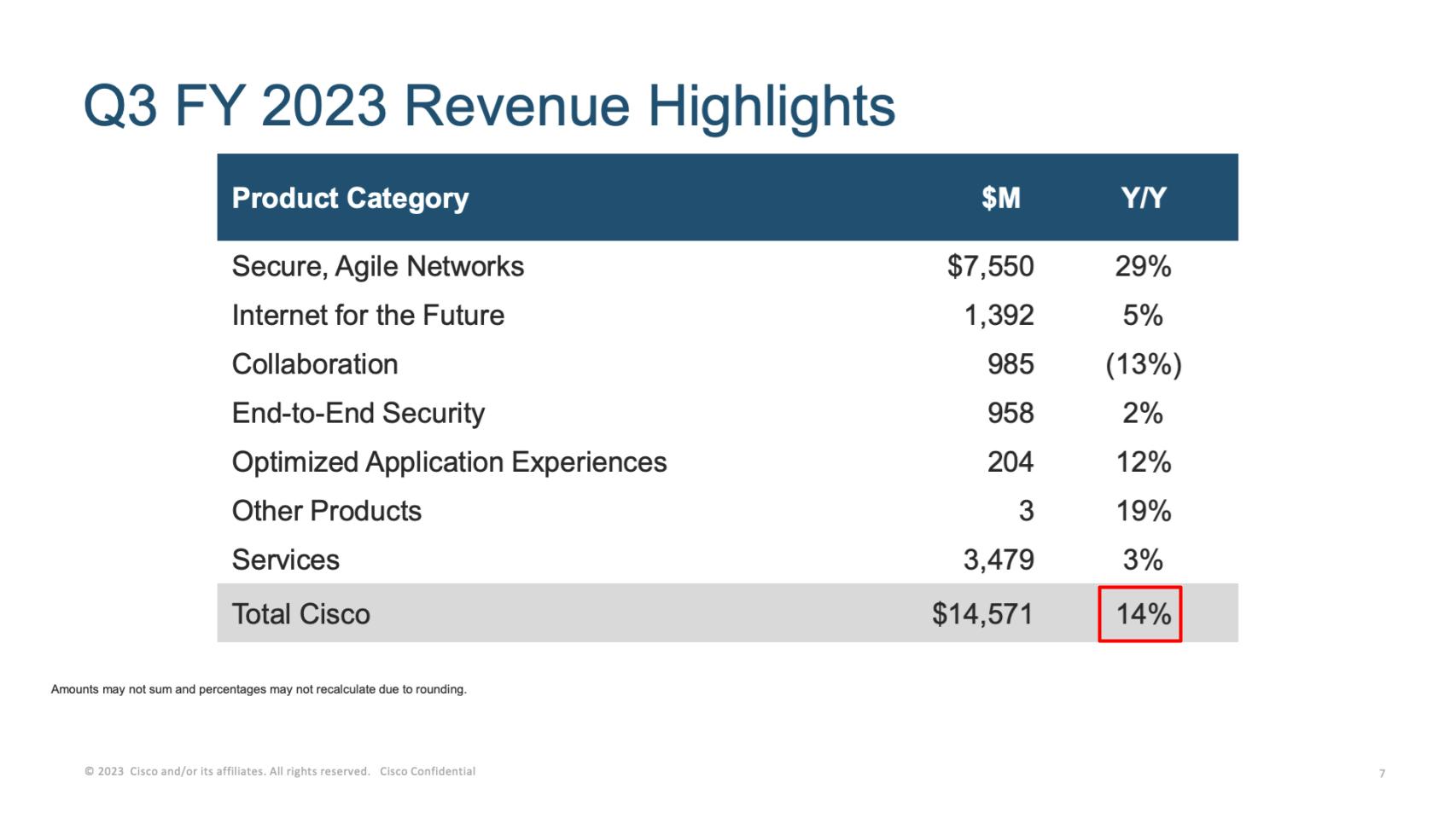
To break this down further, examining Cisco’s 10-K provides the following added context:
Secure, Agile Networks comprise core networking, switching, routing, wireless and compute. This includes products such as Catalyst, Nexus, Meraki and Cisco’s software-defined wide-area network products.
Internet for the Future includes optical networking, 5G, in-house silicon and optics solutions. This includes products such as the Cisco 8000, NCS 5500 and ASR 9000 series.
Collaboration includes Webex and call center solutions.
End-to-End Security comprises network security, cloud security, endpoint, threat management and zero-trust solutions.
Optimized Application Experiences includes AppDynamics, ThousandEyes and Intersight.
Here are Kerravala’s thoughts on Cisco’s portfolio, the challenges they face and what’s needed going forward:
Historically, the IT ecosystem generally has been challenged to create interoperability and cross-platform optimization. Despite its wide array of excellent products, Cisco is an example of a company taking on this challenge. One can point to EMC as a company that was crushed under the weight of its complexity and was forced to sell. IBM deals with its complexity by overlaying a massive service organization on top of its products. Nonetheless, we believe Cisco has an opportunity to address this industry problem head on.
For context, Cisco in the 1990s and beyond experienced tremendous growth, much of it through acquisitions. This created an integration challenge for CEO Chuck Robbins. Relatively early in his tenure, Robbins’ moved to reorganize the executive leadership team to address internal friction and it’s beginning to have a visible impact. As an example, Kerravala cites the unification of the Meraki and Catalyst lines, contributing to simpler execution. Specifically, last year, Cisco enabled customers to view Catalyst devices on the Meraki dashboard. While this took the better part of a decade after the Meraki acquisition, it’s evidence that Robbins is steering the ship in the right direction.
But there’s more work to do. Within Cisco’s own ecosystem, products such as Webex, Meraki and Catalyst have not historically provided a significantly better experience on Cisco’s network than competing products. But that is starting to change under Robbins. Another example of opportunity to watch is Cisco’s portfolio of products such as Kenna, AnyConnect, Talos, Meraki and Catalyst. Today, these do not yet coalesce to form a comprehensive Cisco platform story but we expect that to change in the near term.
In addition, pay attention to the consolidation of mass scale, Internet for the Future, and Secure Agile Networks under Jonathan Davidson, which should lead to better interoperability between the telecom and enterprise sides.
Security under Jeetu Patel is another proof point. For example, the announcement of the XDR solution at the recent RSA Conference is Cisco’s first cross-security solution. Security presents a massive opportunity for the industry to simplify and for Cisco to lead.
The main takeaway is Kerravala posits that Cisco’s focus should be on creating a synergistic portfolio where the collective value exceeds the sum of the parts, as opposed to having to compete fiercely on a product-by-product basis. This he believes will be a sustainable advantage for Cisco.
Watch Zeus Kerravala unpack Cisco’s vast portfolio and how they can simplify.
The ETR spending data for Cisco, at a high level, shows what virtually all tech companies are facing: a decrease in the percentage of customers that are spending more relative to last year.
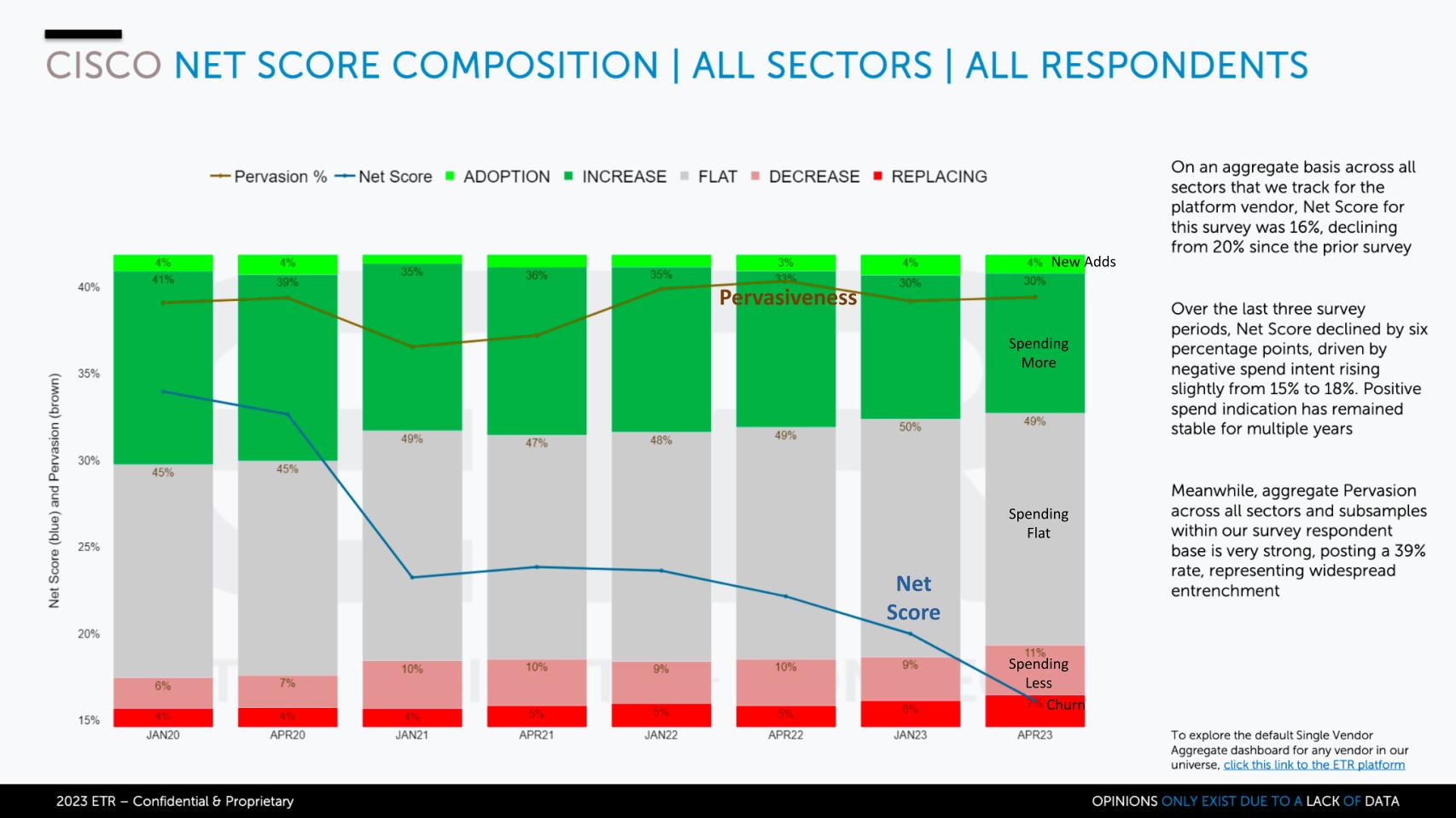
The candlestick chart above shows the granularity of Net Score, ETR’s proprietary spending metric that measures customer spending patterns. Of the 1,700 information technology decision makers in the most recent ETR survey, more than 1,000 are Cisco customers – so we have a nice sample. The lime green is the percentage of those customers adding Cisco new, the forest green represents those spending 6% or more relative to last year, the gray is flat spend, the pink is spending down 6% or worse and the bright red is churn. Subtract red from green and you get Net Score, which is the blue line.
You can see the steadily declining trajectory because of the gray and the reds increasing. The brown line is the pervasiveness in the overall data set, which has actually held up well. Cisco has a massive installed base and it is stable, although more customers are leaving than are being added within this survey. Remember, this survey doesn’t measure spending amount, only the percentage of customers in each bucket.
We asked Kerravala if this accurately reflects his view of the market and is the deceleration a function of economic headwinds, complexity or both? What follows is a list of his key takeaways:
I do think a lot of what you’re looking at there is more credible vendors are in market and that has forced sharper sales execution than it did before. In the old days, Cisco could just show up and be assured that its competitors would mis-execute. That luxury is no longer in play.
Let’s drill into the segment data, starting with networks.
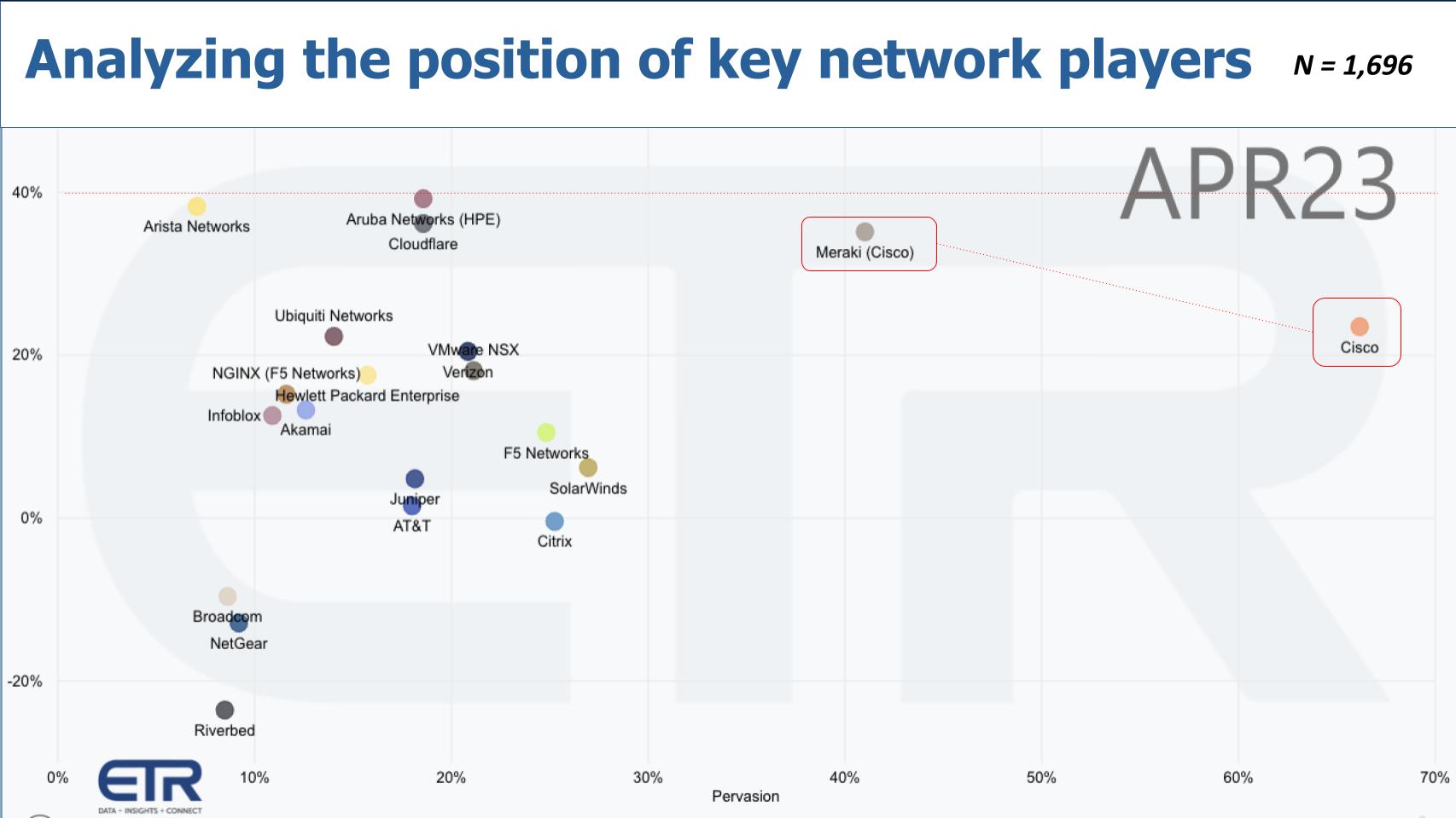
The chart above shows Net Score or spending velocity on the vertical axis and pervasiveness in the data set on the horizontal axis. The red dotted line at 40% indicates a highly elevated Net Score. We’ve highlighted Cisco overall and Meraki, a company Cisco bought in 2012 to help better control network devices.
As is evident, Cisco stands out as the clear leader here in both presence (X axis) with very respectable customer spending velocity on its products (Y axis). In fact, we saw earlier a 29% year-on-year revenue growth figure from last quarter in networking. That is amazing for such a large business. As Cisco works through its backlog, it creates uncertainty in the forecasts, but underlying demand for Cisco’s networking products is sound.
As well, you can see a number of other companies here, including Hewlett Packard Enterprise Co.’s Aruba, Arista, VMware with NSX and a number of others, including Cloudflare Inc., which all are hovering near the elevated 40% line.
Kerravala laid out his thoughts as follows:
He is somewhat critical of Cisco’s approach to its Meraki and Catalyst product lines, not on the merit of their features and value but on the lines between them. He asserts that customers should not have to choose between them. He suggests a unified hardware line that offers customers the flexibility to manage it either through Meraki or the command-line interface, or CLI. Currently, a switch from Meraki to Catalyst necessitates a complete hardware overhaul, a problem that could be resolved by a common set of hardware compatible with both management methods.
Further, Kerravala notes that Cisco’s potential to integrate data center, campus and Wi-Fi certifications to improve the user experience has yet to be fully realized. While some integration has occurred at the campus level, the data center side remains separate. He concludes that networks should deliver applications and experiences as a single, unified entity instead of being sold as separate silos, an approach that contributes to unnecessary complexity.
His key analysis points include:
Watch Zeus break down the Cisco’s networking challenges and thoughts on how it can simplify.
Let’s shift gears and look into the all-important and exceedingly crowded security sector.
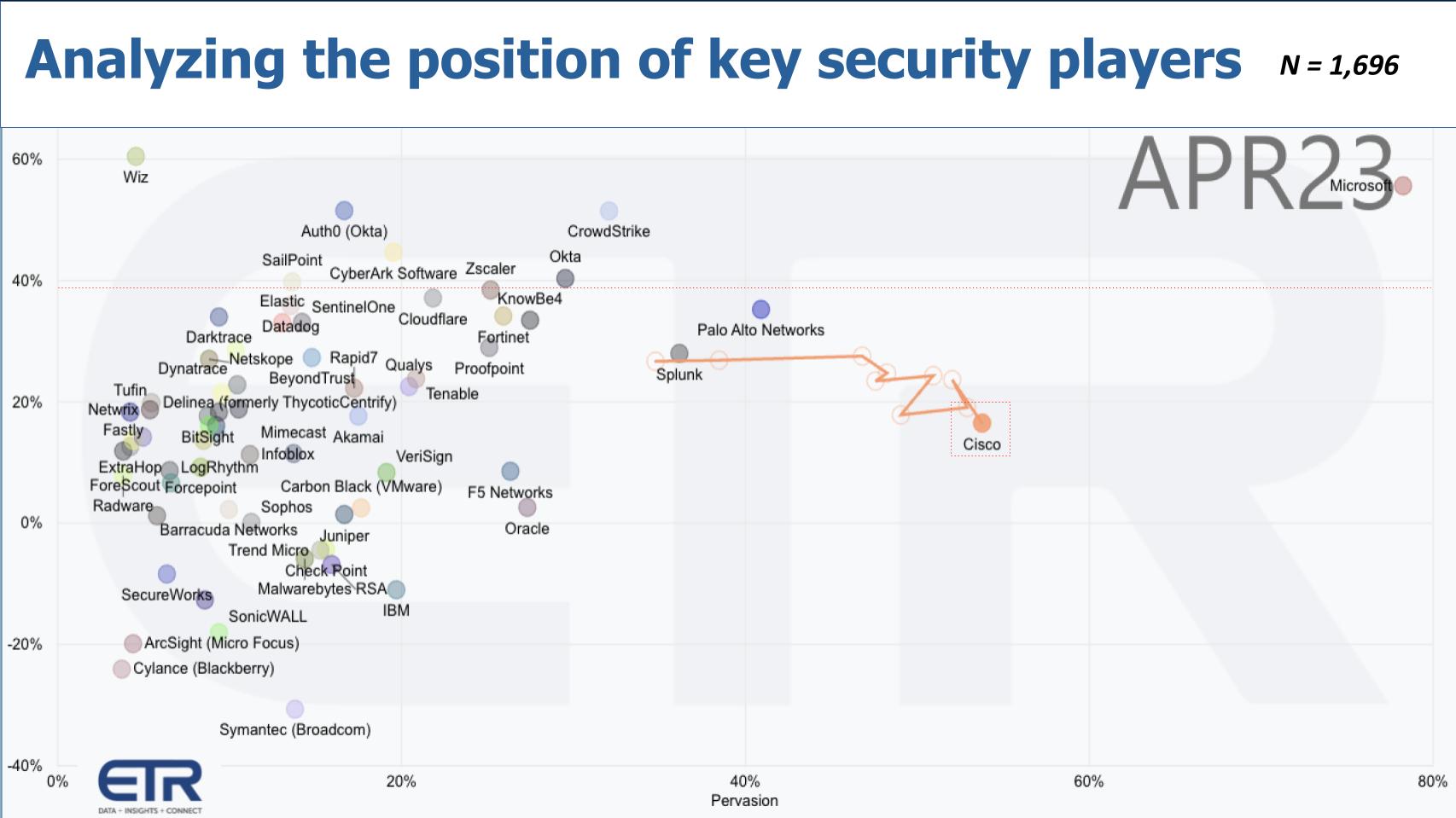
Above we show the ETR spending data in the security market – same dimensions – Net Score on Y and Pervasion on the X. Microsoft Corp. is in the upper right and skews the data, but you can see Cisco has a major presence. As do Palo Alto Networks and Splunk. All credible on the vertical axis.
The leaders in presence are below the 40% line, but that’s expected for such large companies. The squiggly line represents Cisco’s path over the past 10 quarters. There is no debate that the company is very strong in security, but we believe it needs to do a better job consolidating the piece parts and simplifying customer outcomes.
Note that Cisco doesn’t have the spending velocity of the pure plays such as CrowdStrike Holdings Inc., Okta Inc., Zscaler Inc., CyberArk Software Ltd. and SailPoint Technologies Inc. — or even Cloudflare – but its Net Score is respectable. Cisco also just purchased Armorblox Inc., which uses artificial intelligence to reduce email and other risks.
In many ways we think Cisco could be a leader in the security supercloud, bridging on-premises, multiple clouds and edge security experiences.
The following summarizes Keravala’s thoughts:
Kerravala acknowledges Cisco’s success in the security sector, citing notable products such as Kenna, Talos, Umbrella, Duo and AnyConnect. However, he identifies a critical missing element: a more coherent Cisco security narrative. The fact that these products are still referred to individually underscores this problem.
According to Kerravala, the future of security is shifting toward platform-based solutions, moving away from signature-based systems to AI- and analytics-based models. Given Cisco’s broad network reach, the company should possess an unequalled advantage in security, having the ability to detect things that others can’t. Nevertheless, Cisco still needs to integrate its products and offerings better, a process that began with the XDR announcement at the RSA Conference and we believe will continue.
Key takeaways:
In many ways Cisco has been successful in security despite industry complexity and its own complex structure.–Zeus Kerravala
Let’s now dig into observability, which is sort of the confluence of log analytics, application performance management, monitoring and related fields. Cisco has a major stake in this business through its acquisitions of AppDynamics and ThousandEyes.
Before we look at the spending data, here’s what one customer said in an ETR roundtable about this topic:

This is a head of engineering… a customer who says I’m sticking with AppD. This person references the value of the ThousandEyes acquisition along with AppD and security. The application-centricity is an attractive dynamic to this Cisco shop. SecureX is Cisco’s integrated security play, which admittedly needs more and better integration. But basically in the second quote this person calls out the attractiveness and value of a single platform. If you’re a Cisco shop. And if not it’s a “free game” – perhaps implying a free-for-all of complexity.
AppD perhaps presents the biggest opportunity for Cisco since they’ve acquired it. I really expect AppDynamics to become the tip-of-the-arrow sale for Cisco… and I would like to see AppD become a lead sales tool across Cisco’s portfolio. I think it must (and will) happen -Zeus Kerravala
Key takeaways from Kerravala’s commentary on this topic:
Watch Kerravala’s commentary on Cisco’s observability play with ThousandEyes & AppD.
Let’s get into the ETR data. ETR doesn’t have a full-stack observability category, but through this next view below we’re able to bring in various companies that are hovering around the space to see their relative positions.
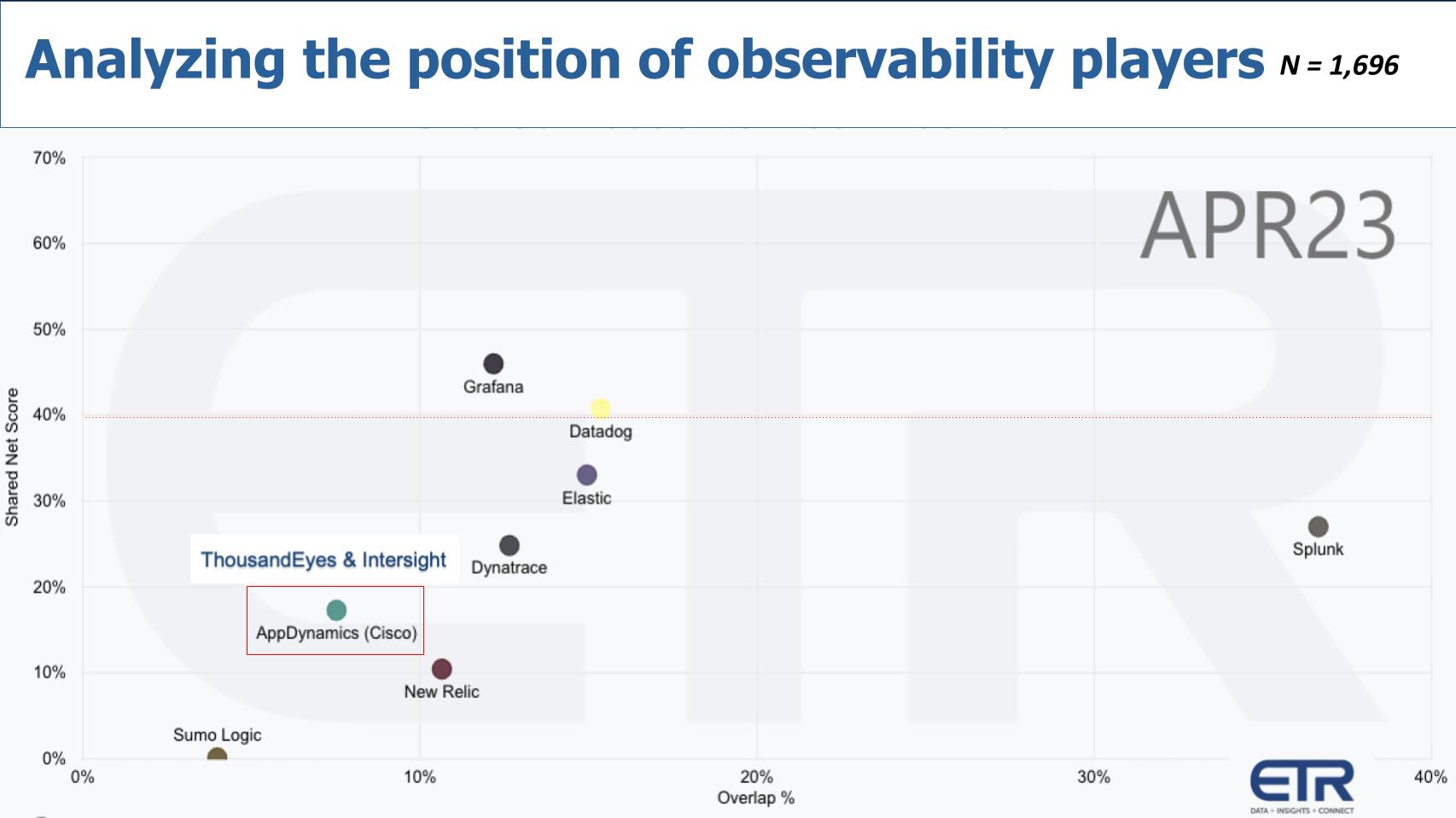
It’s a similar chart above where we show Net Score against pervasiveness in the data. And we’ve plotted Splunk, Datadog Inc., Elastic N.V., Grafana Labs, Dynatrace Inc. and New Relic Inc.. You can see AppDynamics, which Cisco bought in 2017 for almost $4 billion. And it introduced Intersight shortly thereafter as a visualization and orchestration tool. But there were still holes in the portfolio as the market moved to full-stack observability, so Cisco bought ThousandEyes during the COVID pandemic for about $1 billion. Then it sort of strung them together with an overlay, but the story is not over.
Cisco has an opportunity to really take these pieces and integrate them across the portfolio in a potentially game-changing way. At least in the manner that one customer described earlier – especially for Cisco shops.
Kerravala’s primary argument is that the industry needs to to deliver on the vision of full-stack observability. Cisco has an opportunity to lead by streamlining its many panes-of-glass solutions into a unified, intuitive dashboard. The diverse range of visibility tools it currently offers could be more effectively utilized if they were integrated into one comprehensive system, with AppD serving as the principal lens. Operational specifics could then be accessed through drill-down features, allowing for a more organized and efficient user experience. This could be game-changing for Cisco.
Kerravala’s key takeaways on observability:
Kerravala comments on Cisco’s many panes of glass.
Kerravala just published a “Know before you go” post on SiliconANGLE, outlining his thoughts on what to expect at Cisco Live. Let’s review that and what we’ll be looking for next week.

A key question is how Cisco will handle AI. These days, brands run the risk AI washing, but if you bury the AI lede, you look less relevant. In our view, Cisco at the very least has to use AI to make Cisco infrastructure run better and more secure through automation and better management.
Here’s a summary of key points from our conversation with Zeus on what to expect from Cisco Live in terms of AI:
We’ll be watching the security space closely. We believe it’s a mandate that Cisco integrate its vast portfolio across on-prem, all the major clouds and out to the edge. Palo Alto Networks has the leg up on consolidation in our opinion, but Cisco has such a major presence that it can do very well in this area, coming at the problem its strength in networking.
Here’s a summary of what we think Cisco needs to do in security and what we’ll hear at Cisco Live:
Core networking is always a the forefront of Cisco Live. I keep coming back to the supercloud concept – a singular experience across clouds in a cloud-native fashion. Can Cisco bridge the legacy world of apps and infrastructure with cloud-native?
What about collaboration? That business went from rocket ship to rapid deceleration post-pandemic, but hybrid work isn’t going away and it brings real challenges. Is this a game of integrating with your security portfolio to reduce risk? Or creating better and more simplified user experiences? We know that Jeetu Patel wants to make Webex 10 times better than any other platform.
Cisco we think has an opportunity to make some moves in full-stack observability, but the linchpin as Kerravala wrote on SiliconANGLE is the application-centric view of the world. The two main takeaways from our conversation on observability include:
And finally we asked Kerravala if he has ever been to a Cisco Live where Chuck Robbins hasn’t done his part to address environmental, social and governance issues? Here’s a summary of what we discussed:
We didn’t talk much about edge, but it’s a significant part of the future and we anticipate hearing more about it in the future.
Here’s the full conversation about what to expect at Cisco Live
Finally, theCUBE will be at Cisco Live in Las Vegas at the Mandalay Bay. We’re on the expo floor across from the Net Vet Lounge, which is Booth 1427. We have a small space so we’re doing the pop-up CUBE and we’d love to see you. By all means please stop by and say hello.
Many thanks to Zeus Kerravala for stopping by the studio to share his knowledge. Thanks to Alex Myerson and Ken Shifman on production, podcasts and media workflows for Breaking Analysis. Special thanks to Kristen Martin and Cheryl Knight, who help us keep our community informed and get the word out, and to Rob Hof, our editor in chief at SiliconANGLE.
Remember we publish each week on Wikibon and SiliconANGLE. These episodes are all available as podcasts wherever you listen.
Email david.vellante@siliconangle.com, DM @dvellante on Twitter and comment on our LinkedIn posts.
Also, check out this ETR Tutorial we created, which explains the spending methodology in more detail. Note: ETR is a separate company from Wikibon and SiliconANGLE. If you would like to cite or republish any of the company’s data, or inquire about its services, please contact ETR at legal@etr.ai.
Here’s the full video analysis:
All statements made regarding companies or securities are strictly beliefs, points of view and opinions held by SiliconANGLE Media, Enterprise Technology Research, other guests on theCUBE and guest writers. Such statements are not recommendations by these individuals to buy, sell or hold any security. The content presented does not constitute investment advice and should not be used as the basis for any investment decision. You and only you are responsible for your investment decisions.
Disclosure: Many of the companies cited in Breaking Analysis are sponsors of theCUBE and/or clients of Wikibon. None of these firms or other companies have any editorial control over or advanced viewing of what’s published in Breaking Analysis.
THANK YOU